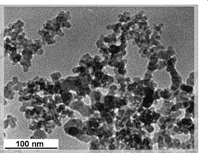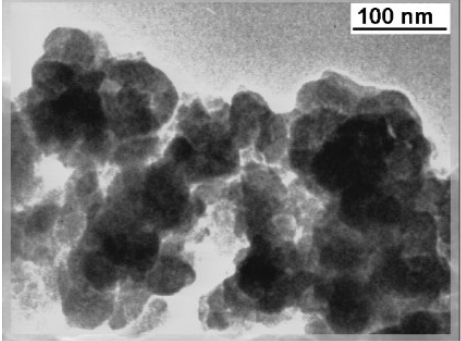
The nanoparticles of carbon were deposited from methane under the potential of a pulsed direct current discharge. The deposition was carried without external heating.
The size, chemistry, and structure of carbon nanoparticles were characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The minimum size of the nanoparticles was as low as 10 nm as shown by TEM.
The nanocrystalline or amorphous structure of the particles was revealed by XRD. Raman spectroscopy indicated on the sp2 bonds of carbon and FTIR spectroscopy identified the other bonds of carbon.
This paper is published in journal of Plasma Processes and Polymers.
Request for PDF:
Contact Address
- ahmadrezarastkar@gmail.com
- +49-17631426313
- +98-9122796476