In this paper, the optical images of glow discharge plasma and the finite element method simulation of the magnetic field strength in a balanced and two types of unbalanced DC circular planar magnetron sputtering sources are presented. The investigation showed that wherever the magnetic field strength is stronger, the intensity of light and the ionization
Plasma electrolytic nitrocarburizing (PEN/C) was applied to the surface of carbon steel under the boiling condition of saturated urea electrolyte. In addition to the general effect of the bath temperature, different applied voltages and processing times were also considered in this new process. Optical and scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, microhardness and pin-on-disc wear tests
Low carbon steel was plasma pack aluminized at 973 K (700 C) for 5, 10, and 15 minutes in vacuum of 15 mbar. A paste of aluminum was packed around the samples, and the process was carried out in glow discharge of argon gas in one step without further diffusion processes. The aluminized samples were
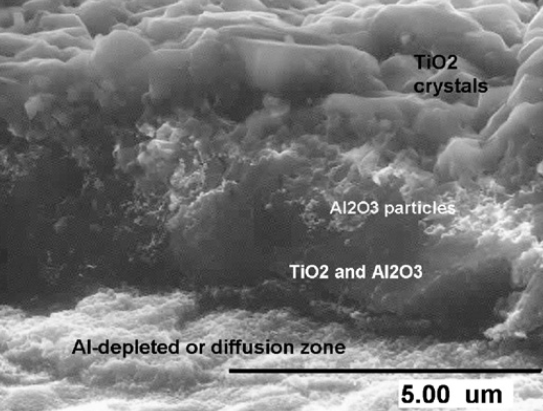
In this investigation, Ti–45Al–2Nb–2Mn–1B (at%) titanium aluminide was thermally oxidised at different tempe ratures of 700–950 ◦C and at different times. Most oxidation exposures resulted in the formation of a compound layer consisting of several oxide layers, a TiO2 layer as the outermost layer on top of a layer of Al2O3 particles, a mixed layer of
Air oxidation, vacuum heating and a subsequent oxidation (DT treatment) of Ti–45Al–2Nb–2Mn–1B (at.%) titanium aluminide resulted in several oxide layers and a hard Ti3Al as an interlayer between the substrate and the oxide layers. Surface characterization was carried out using X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Glow Discharge Spectroscopy (GDS), electron microscopy, microhardness tests, ball-on-disk tests and profilometry.
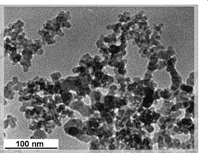
The nanoparticles of carbon were deposited from methane under the potential of a pulsed direct current discharge. The deposition was carried without external heating. The size, chemistry, and structure of carbon nanoparticles were characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The minimum size of the nanoparticles
Microstructure and phase evolution on the surface of Ti–45Al–2Nb–2Mn–1B (at.%) gamma based titanium aluminide was investigated by a series of electron beam melting with different beam energies and scanning speeds. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Glow Discharge Spectroscopy (GDS), Optical Microscopy (OM) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) were performed to characterize the phase modification andmorphology after the
We studied the mechanical properties and wear performance of AISI 1045 (Ck45) carbon steel under the influence of pulsed plasma nitriding. The treatments were performed at temperatures of 500 and 550 C in N2:H2 gas ratios of 1:3 and 3:1 and the working pressure of 10 mbar for 1 to 4 hours. Samples were examined
The surface of Ti-45Al-2Nb-2Mn-1B (at%) titanium aluminide was aluminized in a so called plasma pack aluminizing by packing the substrate in a mixture of aluminum copper alloy and application of an 18 kHz pulsed DC glow discharge plasma in argon gas. The plasma energy provided the necessary heat for melting and mutual diffusion of titanium
Ti–45Al–2Nb–2Mn–1B was plasma enhanced paste aluminized at 800 °C for 30 min with Al–Si alloys, to investigate the effect of silicon on the structure of coatings and oxidation compounds. Optical and electron microscopy revealed fine and coarse particles of blocky and plate like or needle type particles of Ti5Si3 and TiSi2 phases in aluminum or
Ti–48Al–2Nb–2Mn (at.%) alloy was plasma nitrided to investigate the effect of this thermochemical surface modification on the tribological behavior of gamma based titanium aluminides. The effects of nitriding temperature, nitriding time and H2/N2 gas ratio were investigated. Characterization of the microstructure and phases formed within the nitrided surface layers was performed using optical and electron
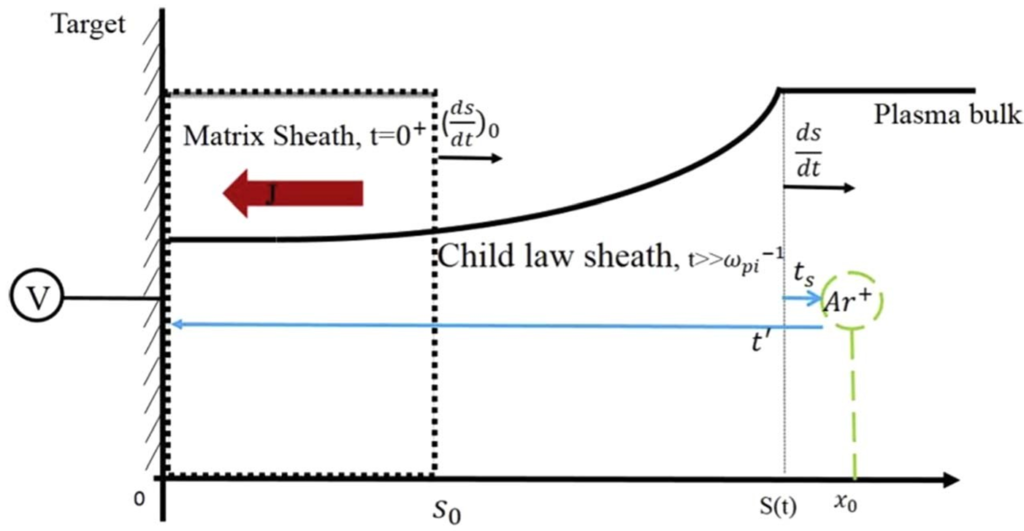
In this work, an analytical model for the time-resolved dynamics of the collisional transient sheath in the plasma source ion implantation (PSII) process is developed. The presented model can forecast the temporal dependence of the implanted ion flux and sheath width in the collisional transient sheath. During the PSII process, the effects of some physical parameters such as
Plasma brazing of gamma based Ti-45Al-2Nb-2Mn-1B titanium aluminide was investigated using Ti-NiCu filler metals. The joints consisted of irregular or equiaxed grain of a2-Ti3Al phases which contained needle-like or fine particles of s3-Al3NiTi2 particles. With increasing Ni from 15 to 25 wt% in filler metals, the shear fracture strength of the joints increased from ~120
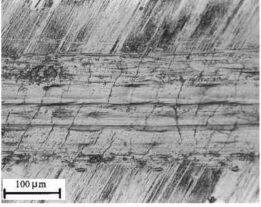
Lamellar Ti–48Al–2Nb–2Mn (at.%) and Ti–45Al–2Nb–2Mn–1B (at.%) titanium aluminides have been wear tested using a ball-on-disc configuration against a 10-mm-diameter hard steel ball under dry sliding conditions at applied loads of 3.5, 5, 10 and 20 N. The worn surfaces have been characterized using optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and microhardness measurements.